심잡음, Heart murmur
심잡음의 개요
- 심장은 우심방, 좌심방, 우심실, 좌심실 2개의 심방과 2개의 심실로 구성되어있다.
- 각 심방 속 피나 심실 속 피나 심장에 붙어 있는 대혈관 속의 피가 각 심방 속이나 심실 속 또는 심장에 붙어 있는 대혈관 속이나 삼첨판, 이첨판, 대동맥 판, 폐동맥판 등 심장 판막, 또는 심방 중격, 심실 중격 등 선천성 심장 혈관 기형 등을 통과해서 흐를 때 특이한 혈류의 잡음이 생길 수 있다.
- 그 혈류 잡음을 심잡음(心雜音)이라 한다.
- 청진기로 심장의 박동을 조심히 들을 때 심장에서 심잡음이 나는지 안 나는지 알 수 있다.
- 심장음에는 심잡음이 없는 심장음과
- 심잡음이 있는 심장음으로 크게 나눌 수 있다.
- 피가 정상적 승모 판(이첨 판), 삼첨판, 대동맥 판, 폐동맥 판 또는 심장에 붙은 혈관 등을 통과할 때 나는 정상 심잡음과, 피가 비정상적인 승모 판, 삼천 판, 대동맥 판, 폐동맥 판이나 심장에 붙어 있는 큰 혈관에 생긴 비정상적 혈관의 부분을 통과할 때, 또는 선천성 심장혈관 기형 부분을 통과할 때 나는 비정상적인 심잡음으로 나눌 수 있다.
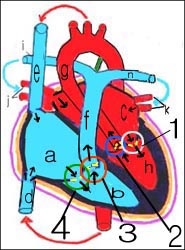
그림 108. 정상 심장 혈관과 판막, 혈류의 흐름
a-우심방, b-우심실, c-좌심방, d-하대정맥, e-상대정맥, f-폐동맥, g-대동맥, h-좌심실, i-우 폐동맥, N-좌 폐동맥, j-우 폐정맥, k-좌 폐정맥
1◯-승모판(이첨판), 2◯-대동맥판, 3◯-폐동맥판, 4◯-삼첨판
소스: Used with permission from Ross lab. Columbus Ohio, USA와 소아가정간호백과
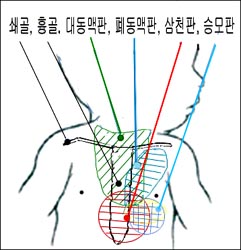
그림 109. 그림으로 표시한 앞가슴 부분에서 대동맥판이나, 폐동맥판, 승모판(이첨판), 또는 삼첨판에서 나오는 심장음이 가장 크고 뚜렷하게 들린다. 또 각 부분에서 들리는 이상 심잡음에 따라 심장의 어떤 부분에 이상이 있는지 진단하는 데 도움이 된다.
Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
- 심잡음이 얼마나 크게 또는 얼마나 작게 나는지 또는 얼마나 높게 또는 낮게 나는지, 심장이 수축 단계와 이완 단계 중 어느 단계에 나는지, 심잡음의 형태, 심장 수축과 심장 이완되는 동안 어느 때에 나는지, 심잡음이 나는 시간의 장단, 가슴 어느 부위에서 가장 크게 심잡음이
- 나는지, 심잡음의 특성, 심잡음이 가슴 어느 부위까지 뻗쳐 나는지, 몸의 자세에 따라 심잡음이 어떻게 변화되는지 등등에 따라 심잡음을 비정상적인 심잡음(병적 심잡음)인지 무해성 심잡음(기능적 심잡음)인지 분별할 수 있다.
- 비정상 심잡음은 심잡음의 특성에 따라 또다시 여러 종류의 심잡음으로 나눌 수 있다. 일반적으로 건강한 아이들 중 30%에게서 정상 심잡음(무해성 심잡음)을 들을 수 있다.
- 스틸 심잡음, 중추성 정맥 험, 무해성 폐동맥 심잡음, 폐동맥 기지성 심잡음 등은 무해성 심잡음의 일종이다.
- 심장이나 심장에 붙은 큰 혈관에 선천성 심장혈관 기형 등 어떤 이상이 있어도 심잡음이 생기지 않을 수 있다.
- 소아청소년들에게 있는 심잡음이 정상 심잡음(무해성 심잡음)일 때는 걱정할 필요 없다.
- 어린자녀에게 정상 심잡음이 있는데도 어떤 종류의 심장혈관 기형으로 생긴 비정상적인 심잡음이라고 잘못 진단받고 일생 동안 그 자녀를 특별히 키울 수도 있다.
- 정상 심잡음은 열이 나든지 감정의 변화, 또는 체위 변화 등에 따라 조금 더 크게, 또는 더 작게 들릴 수 있다.
- 어떤 때는 체위가 변할 때마다 심잡음이 들렸다 안 들렸다 할 수 있다.
- 청진기로 심잡음을 듣고 심잡음이 정상 심잡음인지 비정상 심잡음인지 쉽게 확실히 감별할 수 없는 때도 있다.
- 경우에 따라 심전도 검사, 가슴 X-선 사진 검사, 심 초음파 검사 등 여러 가지 검사를 해서 정상 심잡음과 비정상 심잡음을 확실히 구별할 수 있다.
- 요즘 소아청소년과에서 컴퓨터 디지털 심잡음 레코딩 검사를 받은 후 그 심잡음 레코딩 검사 결과를 소아심장내과 전문의에게 보내 심잡음이 있는지 없는지 알아 볼 수도 있고 심잡음이 있으면 어떤 종류의 심잡음인지 거의 확실히 알 수 있다5.
- 정상 심잡음을 치료할 필요도 없고, 심잡음이 있다고 해서 걱정할 필요도 없다.
- 비정상적인 심잡음이 있으면 심잡음이 나게 하는 원인을 진단해서 그에 따른 치료 한다.
(선천성 심장 기형이 있을 때 주의할 사항 참조)
|
다음은 “심장잡음. 심잡음, 무해성 십잡음, 병적 심잡음”에 관한 인터넷 소아청소년 건강상담 질의응답의 예 입니다. |
Q&A. 심장잡음. 심잡음, 무해성 십잡음, 병적 심잡음
Q.
수고하십니다. 수고하십니다. 제 아기는 생후 1개월 조금 넘었구요. 몸무게는 5kg정도구요. 여아입니다. 수고하십니다. 한달 됐을 때 병원에 갔더니 청진기로 들으니 아기심장에서 약간의 잡음이 들린다고 그러시더라구요. 심장에 구멍이 나면 그럴 수도 있다면서 다음 달에 한번 더 들어보자고 그러셨거든요. 제 아기는 잘 먹고 잘 자는 편인데 왜 그런지요? 혹시 약간의 코감기로 인해 그러는 건 아닌지… 심각한건가요? 심장에 구멍이란 소릴 들으니 너무 걱정이 됩니다. 1>그런 잡음은 다 심장질환과 관계가 있는지요? 그리고 2> 열은 안 나는 데 식은땀을 조금 흘리는 것 같습니다. 왜 그런지요? 자세한 답변 좀 부탁드리겠습니다…
A.
김님
안녕하세요. 좋은 질문해 주셔서 감사합니다. 아이의 나이, 성별, 과거 병력, 가족 병력, 진찰소견, 임상검사 등의 정보를 많이 알수록 답변을 드리는데 도움이 됩니다. 주신 정보를 토대로 해서 답을 드리겠습니다.
Q. 그런지요?
A.
전신에서 돌아온 정맥혈이 상·하대정맥을 통과해서 우심방 속으로 들어오고 우심방 속 피가 삼천판을 통과하여 우심실 속으로 들어가고 그 피가 폐동맥을 통해서 폐 속으로 흘러들어 가는 것이 정상입니다.
폐에서 동맥혈이 폐정맥을 통해서 좌심방 속으로 들어가고 그 피는 좌심실 속을 통해서 대동맥으로 흘러간 다음 전신으로 흘러갑니다. 이것이 정상 혈액순환입니다.
혈액순환 과정에서 피가 심장의 각 부분–우심방, 우심실, 좌심방, 좌심실–등 심장의 2심방, 2심실, 심장에 연결되어 있는 대동맥 판, 폐동맥 판, 또는 폐정맥 등을 통과할 때, 또 삼천판, 이첨판 등을 통과 할 때 혈액 흐름소리가 날 수 있는데 그 소리를 심잡음이라고 합니다.
심잡음은 무해성 심잡음과 병적 심잡음으로 나누어집니다.
정상 심장과 그에 연결되어 있는 정상 혈관에서 정상으로 혈액순환이 될 때 날 수 있는 심잡음을 무해성 심잡음이라 하고
비정상적 심장이나 그에 연결된 비정상 혈관, 심장 판막을 통과해 혈액이 순환 할 때 나오는 비정상적인 심잡음을 병적 심잡음이라고 합니다.
비정상적인 심잡음, 즉 병적 심잡음은 여러 종류의 병적 심잡음으로 나누어지고 그 심잡음이 들리는 크기도 심장이나 혈관의 이상의 종류와 정도와 상태에 따라 다릅니다.
정상 심잡음 즉 무해성 심잡음은 진찰할 때 청진기로 쉽게 들리기도 하고 때로는 들리지 않을 수 있습니다.
아주 작은 비정상 심잡음은 정상 심잡음과 감별하기가 어려운 때도 있습니다.
예를 들면 좌심실과 우심실 사이에 있는 심실중격에 아주 작은 심실 중격 결손이 있을 때는 비정상적 심잡음이 들릴 수 있습니다.
이 때 생기는 심잡음과 정상 심잡음이 확실히 감별되지 않을 수도 있습니다
Q.
혹시 약간의 코감기로 인해 그러는 건 아닌지…
A.
감기로 심잡음이 생기는 것은 아닙니다.
무해성 심잡음이나 병적 심잡음의 크기가 운동, 신체 위치의 변화, 열 등에 따라 변할 수는 있습니다.
Q. 심각한건가요?
A.
작은 심실 중격 결손은 자연적으로 치유가 될 수 있습니다. 그 심잡음이 병적 심잡음인가 무해성 심잡음인가 알아보는 것이 첫째로 할 일입니다.
다음 달에 또 진찰하자고 하셨으니 그 때까지 기다려보시지요
Q. 심장에 구멍이란 소릴 들으니 너무 걱정이 됩니다. 그런 잡음은 다 심장질환과 관계가 있는
지요?
A.
심장에 구멍이 나 있다는 말을 들으면 어떤 부모들도 걱정하는 것은 사실입니다. 위에서 말씀 드린 답변과 같이 병적 심잡음이 있는 어떤 종류의 선천성 심장혈관 기형은 자연히 치료될 수 있으니 희망을 가지시기 바랍니다.
Q.
열은 안 나는 데 식은땀을 조금 흘리는 것 같습니다. 왜 그런지요?
A.
그 정도의 심장 이상으로 땀이 나는 것은 아닌 것 같습니다. 정상적으로 땀이 나는 것 같습니다.
심잡음, 선천성 심장혈관 기형, 심실중격 결손. [부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다– 소아가정간호백과]-제 17권 소아청소년 피부질환–땀이 많이 날 때(다한) 등을 참조하시기 바랍니다. 소아청소년과에서 진찰 진단 치료를 받고 상담하시기 바랍니다. 질문이 더 있으시면 다시 연락 주세요. 감사합니다. 이상원 드림
Heart murmur
Overview of heart murmurs
• The heart consists of two atriums and two ventricles: right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle.
• Blood in each atrium or in the ventricles or in the great blood vessels attached to the heart flows into each of the atria, in the ventricles, or in the great blood vessels attached to the heart, such as tricuspid, bicuspid, aortic, and pulmonary valves, or atrial septum, ventricular septum When flowing through a congenital cardiovascular malformation, etc., a peculiar blood flow noise may occur.
• The blood flow noise is called heart noise.
• You can tell if your heart is murmuring when you listen carefully to your heartbeat with a stethoscope.
• Heart sounds without heart murmur
• It can be broadly divided into heart sounds with heart murmurs.
• Normal heart murmur when blood passes through the normal mitral valve (bicuspid valve), tricuspid valve, aortic valve, pulmonary artery valve, or blood vessels attached to the heart, and abnormal mitral valve, tricuspid valve, aortic valve, pulmonary artery valve or heart murmur. It can be divided into abnormal heart murmurs when passing through a portion of an abnormal blood vessel that is attached to a large blood vessel or when passing through a portion of a congenital cardiovascular malformation.

Figure 108. Normal cardiovascular vessels, valves, and blood flow a-right atrium, b-right ventricle, c-left atrium, d-inferior vena cava, e-superior vein, f-pulmonary artery, g-aorta, h-left ventricle, i-right pulmonary artery, N-left pulmonary artery, j-right pulmonary vein, k -left pulmonary vein
1◯-mitral valve (bicuspid valve),
2◯-aortic valve,
3◯-pulmonary valve,
4◯-tricuspid valve
Source: Used with permission from Ross lab. Columbus Ohio, USA and the Encyclopedia of Pediatric and Family Nursing

Figure 109. Heart sounds from the aortic valve, pulmonary valve, mitral valve (bicuspid valve), or tricuspid valve are the loudest and most distinctly heard in the illustrated prothoracic region. Also, it helps to diagnose which part of the heart is abnormal according to the abnormal heart murmur heard in each part. Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
• How loud or small the heart murmur is or how high or low the heart murmur is, whether the heart is in contraction or relaxation phase, the shape of the heart murmur, when it occurs during contraction and relaxation, and the length of time the heart murmur occurs. , which part of the chest produces the loudest heart murmur
• A heart murmur can be distinguished from an abnormal heart murmur (pathological murmur) or harmless heart murmur (functional heart murmur) according to whether it flies, the characteristics of the heart murmur, to which part of the chest the heart murmur extends, and how the heart murmur changes depending on body posture.
• Abnormal heart murmurs can be further divided into various types of heart murmurs according to the characteristics of heart murmurs. In general, a normal heart murmur (a harmless heart murmur) can be heard in 30% of healthy children.
• Still heart murmur, central venous murmur, innocuous pulmonary artery heart murmur, and known pulmonary arterial murmur are types of innocuous heart murmurs. • Heart murmur may not occur even if there are any abnormalities such as congenital cardiovascular anomalies in the heart or large blood vessels attached to the heart. • If the heart murmur in children and adolescents is a normal heart murmur (innocuous heart murmur), there is no need to worry.
• A young child who has a normal heart murmur may be mistakenly diagnosed as an abnormal heart murmur caused by some kind of cardiovascular malformation and may be specially raised for the child for the rest of her life.
• A normal heart murmur may sound a little louder or lower depending on a fever, a change in emotion, or a change in position.
• Sometimes, whenever you change your position, you may hear a heart murmur or not.
• There are times when it is not easy to clearly determine whether a heart murmur is a normal heart murmur or an abnormal heart murmur by listening to a heart murmur with a stethoscope.
• In some cases, various tests, such as an electrocardiogram, chest X-ray, and echocardiography, can be performed to clearly distinguish between a normal heart murmur and an abnormal heart murmur.
• These days, after receiving a computer digital heart murmur recording test at the Department of Pediatrics, the results of the heart murmur recording test can be sent to a pediatric cardiologist to find out whether a heart murmur is present or not, and if there is a heart murmur, it is almost certain to know what kind of heart murmur5.
• There is no need to treat a normal heart murmur, and there is no need to worry if you have a heart murmur.
• If there is an abnormal heart murmur, diagnose the cause of the heart murmur and treat it accordingly. (See Precautions for Congenital Heart Anomalies) Next is “Heart murmur.
This is an example of Internet pediatric health counseling Q&A on “heart murmur, innocuous ten murmur, and pathological heart murmur”.
Q&A. heart murmur. Heart murmur, innocuous ten murmur, pathological heart murmur
Q. You are working hard. You are working hard. My baby is just over 1 month old. It weighs about 5 kg. girl. You are working hard. When I was a month old, I went to the hospital and they told me that when I listened to it with a stethoscope, I could hear a little noise in the baby’s heart. He said that if there is a hole in the heart, it might be the case, and we will listen again next month. My baby eats and sleeps well, but why? Maybe it’s because of a slight cold… Is it serious? I’m so worried about hearing about a hole in my heart. 1>Are all these noises related to heart disease? And 2> I don’t have a fever, but I seem to be sweating a little. Why? Please give me a detailed answer..
. A. Kim Hello. Thanks for the nice question. The more information you know, such as the child’s age, gender, past medical history, family history, examination findings, and clinical examination, it will help you to give an answer. We will give you an answer based on the information you have given us.
Q. Is that so?
A. It is normal for the venous blood returned from the body to pass through the superior and inferior vena cava and enter the right atrium, the blood from the right atrium passes through the three-thousand plate into the right ventricle, and the blood flows into the lungs through the pulmonary artery. Arterial blood from the lungs enters the left atrium through the pulmonary veins, and the blood flows through the left ventricle into the aorta and then throughout the body. This is normal blood circulation.
During the blood circulation process, when blood passes through each part of the heart – right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle – etc.
When passing through , bicuspid, etc., the sound of blood flow may be heard, which is called a heart murmur. Heart murmurs are divided into innocuous heart murmurs and pathological heart murmurs. A heart murmur that can occur when blood circulates normally from a normal heart and the normal blood vessels connected thereto is called a harmless heart murmur. An abnormal heart murmur that occurs when blood circulates through an abnormal heart, abnormal blood vessels connected to it, or heart valves, is called a pathological heart murmur. Abnormal heart murmurs, that is, pathological heart murmurs, are divided into several types of pathologic heart murmurs, and the size of the heart murmurs varies depending on the type, degree, and condition of the heart or blood vessel abnormalities. A normal heart murmur, or innocuous heart murmur, may or may not be heard easily with a stethoscope during examination.
A very small abnormal heart murmur is sometimes difficult to differentiate from a normal heart murmur. For example, an abnormal murmur may be heard when there is a very small ventricular septal defect in the ventricular septum between the left and right ventricles. A heart murmur that occurs at this time may not be clearly differentiated from a normal heart murmur.
Q. Maybe it’s because of a bit of a cold…
A. A cold does not cause a heart murmur. The size of an innocuous or pathologic murmur may change with exercise, changes in body position, or heat.
Q. Are you serious?
A. Small ventricular septal defects can heal spontaneously. The first thing to do is to determine whether the heart murmur is a pathological or harmless heart murmur. You said we’ll see you again next month, so please wait until then.
Q. I’m very worried when I hear that there is a hole in my heart. All of these noises are related to heart disease. right?
A. It is true that some parents are concerned when they hear that they have a hole in their heart. As mentioned above, some types of congenital cardiovascular anomalies with pathologic heart murmur can be cured naturally, so please have hope.
Q. I don’t have a fever, but I seem to be sweating a little. Why?
A. I don’t think I’m sweating more than that much heart rate. You seem to be sweating normally. Heart murmur, congenital cardiovascular malformation, ventricular septal defect. www.drleepediatrics.com – Vol. 17 Skin diseases in children and adolescents – When sweating profusely (Dahan), etc. Please consult with the Department of Pediatrics for diagnosis, diagnosis and treatment. If you have any more questions, please contact us again. thank you. Lee Sang-won Dream
출처 및 참조 문헌 Sources and references
- NelsonTextbook of Pediatrics 22ND Ed
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 22ND Ed
- Growth and development of the children
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- Neonatal Resuscitation, American Academy Pediatrics
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제22권 아들 딸 이렇게 사랑해 키우세요
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제23권 사춘기 아이들의 성장 발육 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제24권 소아청소년 성교육
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제25권 임신, 분만, 출산, 신생아 돌보기
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원 저
- The pregnancy Bible. By Joan stone, MD. Keith Eddleman, MD
- Neonatology Jeffrey J. Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- 임신에서 신생아 돌보기까지. 이상원
- Breastfeeding. by Ruth Lawrence and Robert Lawrence
- Sources and references on Growth, Development, Cares, and Diseases of Newborn Infants
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Neonatal resuscitation Ameican academy of pediatrics
- Pediatric Nutritional Handbook American Academy of Pediatrics
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
-
Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
-
Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
-
Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A.
- 제4권 모유, 모유수유, 이유 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유, 비타민, 단백질, 지방 탄수 화물 참조문헌 및 출처
- 제6권 신생아 성장발육 양호 질병 참조문헌 및 출처
- 소아과학 대한교과서
Copyright ⓒ 2014 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances.
“Parental education is the best medicine.